AVR microcontroller
AVR microcontroller
Features of AVR microcontroller
- This module performs numerous functions that have two-directional inputs and output ports which can be configured with the pull-up resistances.
- There are numerous inner oscillators, consisting of RC oscillators also exits on this board.
- Internal data EEPROM up to 4 KB
- Internal SRAM up to 16 KB
- Multiple power-saving sleep modes
- Lighting and motor control (PWM-specific) controller models
- There is a flash memory of 250 kilobyte storage space exits on this board.
- The static random access memory having space of sixteen kilobytes is exist on this board.
- There are 2 timers of eight bit and sixteen-bit exits on this board.
- The pulse width modulation output exists on this board.
- There is an analog comparator also assembled on this module
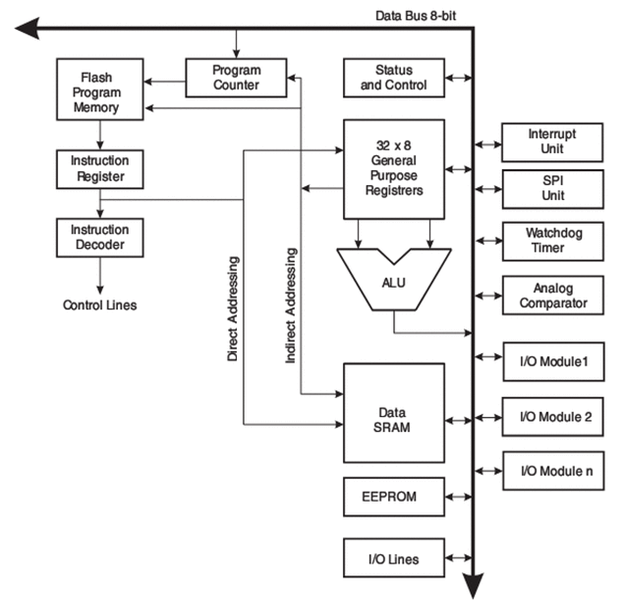
Data BUS 8 bit: Its an 8-bit parallel data lines by which the data travels inside the MCU (NOTE: this is the reason why AVR is an 8-bit MCU).
ALU: Arithmetic Logic Unit, the core/heart of the entire system where typically all commands get executed.
Data SRAM: It basically pretty similar to the RAM (Random access memory) we see inside our computers.
EEPROM: (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory) its very similar to another component in our computer namely Hard Disk, i.e. a permanent storage.
I/O lines: These are the bunch of registers which is used as a switches or controls for different features of AVR.
32X8 GPR (General Purpose Registers): This are 32 registers each having 8-bit which is a general storage space for data. But, remember, SRAM is also a temporary storage but these registers have some specialty among all.
Status & Control: A couple of registers which are very special to the MCU & to us also.
Program Counter: This is a register which has a responsibility to track the position of the program that is currently executing.
Flash Memory: It is also a permanent storage but its only for storing the program we write to it.


Recent Comments