Core Less Induction Furnace
The core less induction furnace operates on the same principle of an electric transformer.
The eddy currents developed in any magnetic circuit are given by the equation
eddy currents α B2 f2 (B = maximum flux density (T), f = frequency (Hz))
In coreless furnace, there is no core and thus flux density will be low.Compensating the low flux density, the primary current applied to the primary coil should have sufficiently high frequency(500-1000Hz).
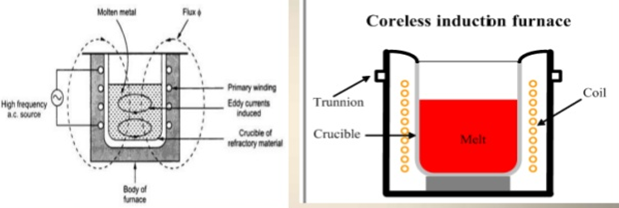
- It consists of a coil, it is wound around the crucible. This coil acts as primary of a transformer.
- Charge to be melted acts as the secondary of the transformer. Charge is placed in cylindrical in shaped ceramic crucible (Refractory).
- When supply is given to primary coil, it produces eddy-currents in the charge or crucible by transformer action. These currents heat the charge to melting point and they also set up electromagnetic forces which produce a stirring action in the charge.
- Due to high frequency of the supply, the skin effect in the primary coil increases the effective resistance of the coil and the copper loss. To reduce copper losses, hollow copper conductors are used in which cold water is circulated.
Application- melting of steel and other ferrous metals
Advantages
- High speed of heating.
- Low erection and operating costs.
- The automatic stirring action produced by eddy currents.
- Well suited for intermittent operations
- Their charging and pouring is simple.
- Precise temperature control.
- They can be used for all industrial applications requiring heating and melting.
- Most suitable for the production of high-grade alloy steels.



Recent Comments