Electric Supply For Traction
The three main types of electric traction systems that exist are as follows:
- Direct Current (DC) electrification system
- Alternating Current (AC) electrification system
- Composite system.
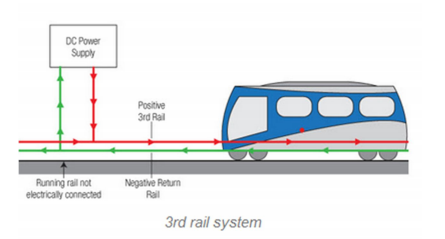
Direct Current (DC) electrification system : DC supply is supplied to the vehicle through two different ways, the first way is through the 3rd rail system (side running and under running electrified track and providing return path through running rails),and the second way is through the overhead line DC system. This DC is fed to the traction motor like the DC series or compound motors to drive the locomotive, as shown in the below figure.
Alternating Current (AC) electrification system: In AC traction system has become very popular nowadays, and it is more often used in most of the traction systems due to several advantages, such as quick availability and generation of AC that can be easily stepped up or down, easy controlling of AC motors, less number of substations requirement, and the presence of light overhead catenaries that transfer low currents at high voltages, and so on.
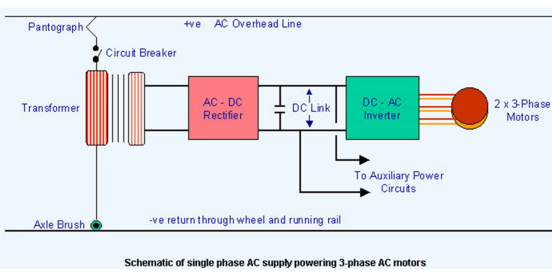
The supply systems of AC electrification include single, three phase, and composite systems. The Single phase systems consist of 11 to 15 KV supply at 16.7Hz, and 25Hz to facilitate variable speed to AC commutation motors. It uses step down transformer and frequency converters to convert from the high voltages and fixed industrial frequency. The Single phase 25KV at 50Hz is the most commonly used configuration for AC electrification. It is used for heavy haul systems and main line services since it doesn’t require frequency conversion. This is one of the widely used types of composite systems wherein the supply is converted to DC to drive DC traction motors.
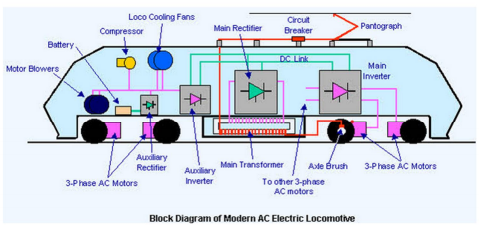
An electric motor speed controller is used by varying the voltage applied to it. The Special drive systems that are used to control these electric motors include tap changer, thyristor control, chopper control and micro processor control drives.
The disadvantages of this system include difficulty in interruption of currents at high voltages when fault condition is raised, and the need for locating DC substations between short distances.
Composite system: This system incorporates the advantages of both DC and AC systems. These systems are of mainly two types: a single phase to three phases or Kando system, and the other single phase to DC system.
In a Kando system, a single overhead line carries the single-phase supply of 16KV, 50Hz. This high voltage is stepped down and converted to three-phase supply of same frequency in the locomotive itself through the transformer and converters



Recent Comments