Electrolysis
Electrolysis
- Process of chemical change taking place in a electrolyte by the passage of electricity is called Electrolysis
- It is a process of decomposition of an electrolyte substance, which is present in liquid state, when current is passed through it. The process of electrolysis takes place in cell known as electrolytic cell.
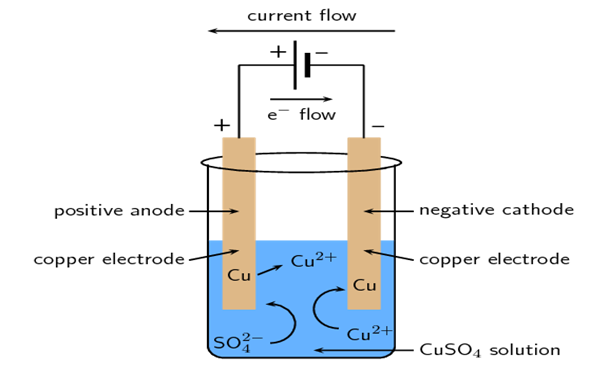
- It consists of a container, that contains an electrolytic solution ie, dilute solution of copper sulphate CuSO4. The electrolyte dissociated into copper and sulphate ions.The cell contains conducting plate called electrode. Copper plates are taken as electrode. Electrode connected to the positive terminal of the supply is called Anode. Electrode connected to the negative terminal of the supply is called cathode. Electrodes are connected to a source of power supply(DC).
- Due to applied potential across electrodes an electric field set up in the electrolyte and it exerts electric forces on the ions and cause them to move. The positively charged ions CU++ are attracted towards negative charged electrode that is cathode and SO4 moves towards anode. The current through the electrolyte is carried by these two moving streams of ions.
- When ions arrive at the electrodes, due to the energy of the battery, their charges are neutralized and ions become atoms. Thus when CU++ move to cathode, they leave their charge and become Cu atoms which are deposited over the cathode. Similarly SO4 moves towards anode and give up the charge there. If the anode is of copper then sulphate will react with it to form CuSO4.
- The whole process describe above is called Electrolysis.
Fraday’s laws of Elctrolysis
Faraday’s two laws stated as follows:
First law : The amount of material deposited or liberated over an electrode in an electrolytic cell is propotional to the quantity of electricity which has passed through it.
i.e. mass of chemical deposition,
m α Q , m α It , m = Zit
where Z is a constant depending upon the substance.
Second law : The amounts of chemical changes produced by the same quantity of electricity in different substances are proportional to their equivalent weights.
The equivalent weight = Atomic weight / Valency = a/v
Where, a = atomic weight & v = valency
Application of Electrolysis
- Electroplating: It is a process of coating a thin film of a metal over a base metal by the passage of current in the electrolyte and for the protection of base metal from corrosion.In this method pure metal is to be used in coating, as anode and base metal take as cathode along with a suitable electrolyte.
Eg: Gold coated over a copper plate.
- Extraction of metals: In this process. The ores are subjected to electrolysis to extract metals.
Eg: Aluminium Extraction from Bauxite ore
- Purification of metals: Metals can be purified by electrolysis. In the purification of metals, the impure metal is used as anode and the pure metal plate is used as a cathode. When electricity is passed, the impure metal gets dissolved and pure metal gets deposited on the cathode.
- Electrotyping: It is used in preparing blocks used in printing.
- Production of chemicals: Various chemicals are produced with the help of electrolysis. Caustic soda, chlorine….
- Galvanization: It is the Process of coating a metal usually iron/steel, with a protective covering of zinc.
- Anodizing: Anodizing protects aluminum with a durable, attractive finish. In this process to coat aluminium or magnesium with a thin layer of oxide to help prevent corrosion.



Recent Comments