Soil Resistivity
Soil resistivity is a measure of how much the soil resists or conducts electric current. Thus before designing and installing a new grounding system in an electrical substation, the location should be tested to find out the soil’s resistivity. The SI unit of resistivity is the Ohm-meter (Ω-m).
Measurement of Soil resistivity,
- Wenner method
- Schlumberger method
Wenner method:
The Wenner four-pin method is the most commonly used technique for soil resistivity
measurements. In this method the four spikes arranged in the straight line are driven into the soil at equal distance. A known current is passed between electrode C1 and C2 and potential drop V is measured across P1 and P2. The current I develop an electric field which is proportional to current density and soil resistivity. The voltage V is proportional to this field. This voltage and current is measured.
Using the Wenner method, the apparent soil resistivity value is,
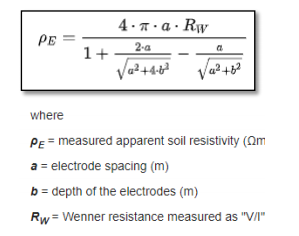
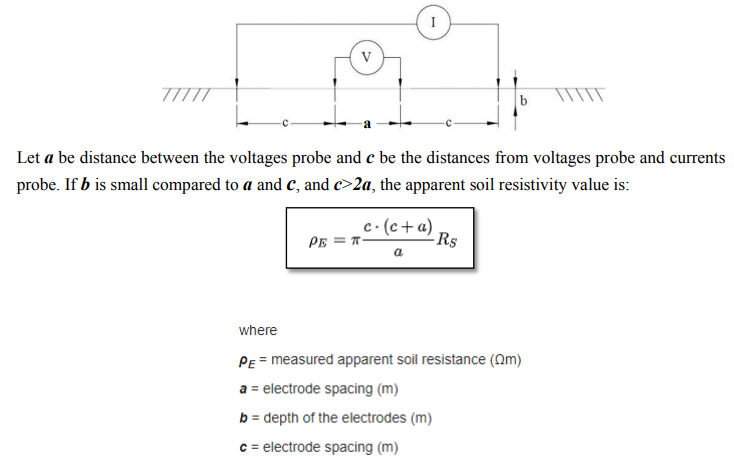
Schlumberger method:



Recent Comments