Differential Protection of Alternators or Merz-Price circulating current protection
- Differential protection or Mertz Price circulating current is mainly employed for the alternator stator winding protection against earth faults and phase-to-phase faults by use of circulating current principle.
- It function on the concept of comparing the two currents in and out of stator coil. In normal condition the two current will be same, if fault occurs there will be some difference , The difference of the currents under fault conditions is arranged to pass through the operating coil of the relay. The relay then closes its contacts to isolate protected section from the system.
Arrangement for Differential Protection System
The protection system requires two identical transformers CT1 & CT2 which are mounted on both sides of the stator windings.So for three phase there are six no of CT’s. The secondaries of all CT’s are connected in star and other winding of each CT’s set are connected through cable called pilot cable.Three coil are connected in pilot cable. They are connected in a equipotential point of pilot cable.The equipotential point of the pilot wire is its centre, so the relay is located at the midpoint of pilot wires. The relay coils are connected in star. The neutral of the current transformer and the relay are connected to the common terminal.The relays are generally of electromagnetic type.

Working:
Under normal condition, the current at both ends of each winding will be equal and there will be no current difference in two sides of protected zone, hence Two ct’s in a phase will conduct same current. ie, there is a balanced circulating current in the piolet wires and no current flows through the operating coils(R1,R2,R3).
- Earth fault occurs on the R phase of the network because of the insulation breakdown to earth. current in that phase will flow through the core and frame of the machine to earth, the circuit being completed through the neutral earthing resistance. The current in the secondary of the transformer becomes unequal. The differential currents flow through corresponding relay coil. Thus, the relay becomes operative and gives the command to the circuit breaker for operation.
- Short circuit fault occurs between any two phases, say Y and B then short-circuit current flows through these phases. The fault unbalanced the current flows through CTs. The differential current flows through the relay operating coil and thus relay trips their contacts.
Problems Associated with Differential Protection System
A neutral resistance wire is used in the differential protection system for avoiding the adverse effect of earth fault currents. When an earth fault occurs near the neutral, it will cause a small, short circuit current to flow through the neutral point because of small emf. This current is further reduced by the resistance of the neutral grounding. Thus, the small current will flow through the relay. This small current will not operate the relay coil, and hence the generator gets damage.
Modified Differential Protection System for Alternators
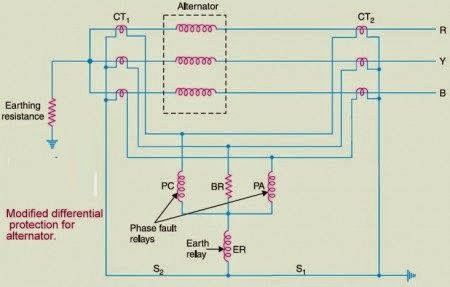
To overcome the above problem, the modified scheme has been developed. In this scheme two elements are arranged, one for the protection of the phase fault and other for the earth fault protection.The phase elements are connected in stars along with the resistor. The earth fault relay is kept between the star and neutral. The two-phase elements together with a balancing resistor are connected in star, and the earth fault relay is connected between the star and neutral pilot wire.
Related Terms



Recent Comments