Electric Drives – Block Diagram
An electric drive can be defined as an Electro-mechanical device for converting Electrical energy to mechanical energy to impart motion to different machines and mechanism for various kinds of process control. It is the combination of prime mover, controlling device, transmission equipment and mechanical working load, electric motor used as a prime mover.
Advantages of Electric Drives
- They have a longer life span than other drives systems.
- They are pollution free & clean due to absence of fuel, fumes etc.
- It is more economical.
- Electrical energy is transmitted easily.
- The noise level of electric drive is less.
- No need of any fuel storage and transportation.
- It has High efficiency.
- Regenerative braking is possible only in electric drives.
- Various speed control methods available.
- They require less space.
- It is reliable and economical source of power.
- It can be remotely controlled.
- Available in wide range of various parameters like speed, torque, and power.
- Electrical energy can be transported to long distances by transmission lines.
Disadvantages of Electric Drives
- It cannot be installed where electricity is not available. For installation of electric motor electrical energy is necessary.
- On the failure of electrical supply, the electrical drive system cannot work.
- It can cause noise pollution.
- The initial cost of the system is high.
Block Diagram of Electric Drive
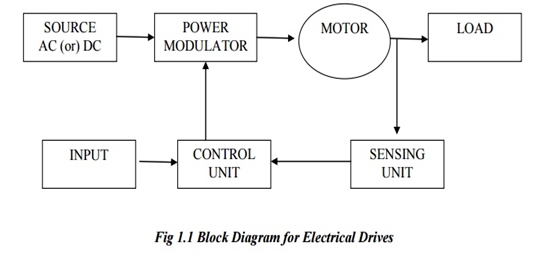
It basically consists of the following components,
- Source : A source can be anything AC or DC used in the system. 1 -Φ or 3 Φ, 50 Hz Ac is mostly used in the drive system in most locations.
- Power modulator: The main function of power modulator is to modulate the flow of power from a source to the motor. It modulates the power as per torque-speed characteristics required by the load. It regulates source and motor currents within some required value. It regulates the current in starting, braking and some speed reversal conditions.
- Electric motor: Motor is generally used in the system to convert electrical of energy into electrical energy. Motors used in electric drives are induction motors. Synchronous motors, Dc motors, stepper motors and also reluctance motors.
- Mechanical load: Load can be anything which consumes power. It is machinery, such as fans, blowers, pumps, robots and machines which performs a given task.
- Sensing unit: This unit is consists of current sensor or speed sensor. It senses the output speed or required quantity. Speed is sensed in the system by tachometer which is coupled with the motor. Current sensing is required in the system for current limit control. Sensing unit is directly attached to the controlling unit.
- Control unit: Sensed Output is given to the controlling unit. In controlling unit, Sensed output and required output is compared and some input command given to the controller for getting the required output. Various types of controllers are used in electric drives. Control unit controls the function of power modulator.
- Power transmission ( coupling/gear box /Chain /belt..)
Factors governing selection of motor for an Electric Drives
- Nature of supply: AC Supply / Pure DC Supply /Rectified DC
- Electrical characteristics : Starting characteristics, Running characteristics, Speed control, Braking characteristics
- Mechanical characteristics : Nature of load, Noise level, Cooling system, Types of bearing, Methods of power transmission, Types of enclosure.
- Nature of drive: Individual , Group drive
- Size and rating of motors : Whether the motor is to drive continuous, intermittent, or variable load cycle.Whether its over load capacity and pull out torque are adequate.
- Cost : Capital cost & Running cost.



Recent Comments