Methods of Cable laying of Underground cable
Explain the three methods of Cable laying of Underground cable with necessary sketches?
There are three main methods used for laying underground cables.
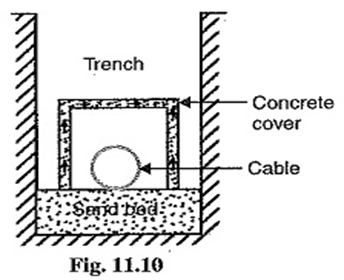
1. Direct laying:
- A trench of about 1.5 meter deep and 45cm wide is dug. Then the trench is covered with a layer of fine sand, about 10cm thick the cable is laid over the sand. The sand does not allow the entry of moisture from the ground.
- Cable must have serving of bituminized paper and hessian tape as to provide protection against corrosion and electrolysis. Then the cable is covered with another layer of sand of about 10cm thickness.
- After that the trench is covered with bricks and other materials to protect the cables from mechanical injury.
- When more than one cable is to be laid in the same trench, a horizontal or vertical inter axial spacing of at least 30cm is provided in order to reduce the effect of mutual heating and also ensure that a fault occurring on one cable does not damage the adjacent cables.
- This method of laying underground cables is simple and cheap.
- Disadvantages: Maintenance cost is very high. Localisations of fault is difficult. Alteration in the cable network cannot be made easily.
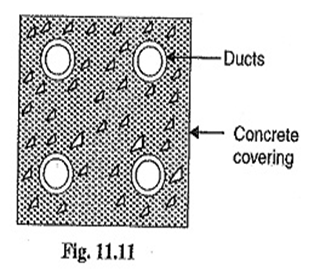
2. Draw-in system:
- This method of cable laying suitable for congested areas where excavation is inconvenient.
- In this method a line of conduits, ducts or tubes made of either iron, glazed stoneware clay or cement concrete are laid in ground with manholes at suitable positions along the cable rotate. The cables are then pulled in to position.
- Separate pipes and ducts are provided for each cable laid in the same duct. Care must be taken that where the duct line changes direction, depths, so that a large cable may be pulled easily between the manholes.
- The distance between the manholes should not be too long so as to simplify the pulling in the cables.
- Three of the ducts carry transmission cables and fourth duct carries relay protection connection, pilot wires.
- Cables not need armouring but must be provided with serving of hessian and jute in order to protect them when being pulled into the ducts.
- Advantages: Less chance of fault occurrence, Less Maintenance cost, Easy repairs, Easy alterations
- Disadvantages: Initial cost is very high.
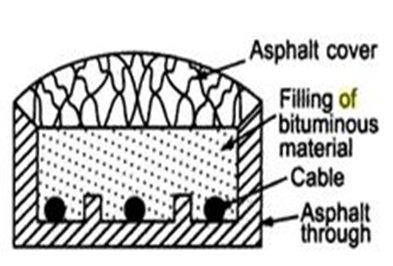
3. Solid system:
- In this method the cable is laid in open pipes or troughs dug out in earth along the cable route.
- The toughing is of cast iron, stoneware, asphalt or treated wood. After laying the cable in position, the toughing is filled with a bituminous and covered over.
- More expensive than direct laying & Requires skilled labours.





Recent Comments