Nuclear Power Station Working
Nuclear Power Station
A generating station in which nuclear energy is converted into Electrical energy is known as Nuclear Power Station.
A nuclear power plant is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. Nuclear power plants heat produced during nuclear fission process. Heavy elements such as Uranium 235 & Thorium 232 are subjected to nuclear fission in a special apparatus known as reactor. The heat generated by nuclear fission is used to generate high temperature & pressure steam that drives a Steam turbine connected to a generator that produces electricity.
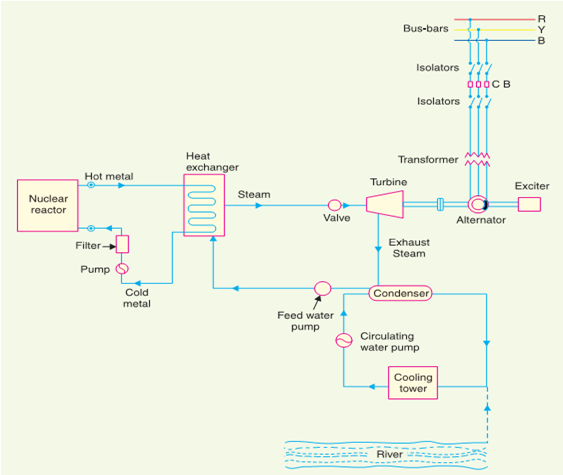
Main components of nuclear power plants:
- Nuclear Reactor: It is an apparatus in which nuclear fuel (U235) is subjected to nuclear fission. It controls the chain reaction that starts once the fission is done. If the chain reaction is not controlled, the result will be an explosion due to the fast increase in the energy released.
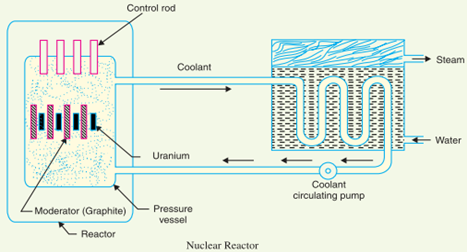
A nuclear reactor is a cylindrical stout pressure vessel and houses fuel rods of uranium, moderator & control rods. The fuel rods constitute the fission material and release huge amount of energy when bombarded with slow moving neutrons. Moderator consists of graphite rods/Heavy water which enclose the fuel rods. Moderator slow down the neutrons before they bombard the fuel rods. The control rods are of Boron / Cadmium are inserted into the reactor. Cadmium is a strong absorber of neutron and thus regulates the supply of neutrons for fission process according to the load variations. When the control rods pushed in deep, they absorb almost all neutrons and stops the chain reaction ie, the stops. The heat produced in the reactor is removed by the coolant, generally sodium metal and water is used. The coolant carries the heat to the heat exchanger.
2. Heat exchanger: The coolant gives up heat to the heat exchanger which is utilized in raising the steam. After giving up heat, the coolant is again fed to the reactor by use of pump.
3. Steam turbine: The steam produced in the Heat exchanger is passed to the turbine through a valve and work is done by the expansion of steam in the turbine. Exhaust stem from turbine is passed to the condenser. Condenser condenses the steam which is fed to the heat exchanger through feed water pump.
4. Alternator: The steam turbine is coupled to the alternator. The alternator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. The output from the alternator is given to the bus-bars through transformer, circuit breakers and isolators.



Recent Comments