Resistance
Resistance:
The opposition offered by a substance to the flow of electric current is called resistance. The resistance offered by the circuit elements is essential to limit the flow of current. Resistance Unit is Ohm.
The laws of resistance states that the Resistance “R” offered by a conductor depends upon following factors, ρ = resistivity, L= length of conductor, A= area of conductor
R =ρ L /A
- The Resistance “R” is directly proportional with it’s length “L”
- The Resistance “R” is Inversely proportional with it’s Cross Sectional Area: “A”
- The Resistance “R” is dependent on the Nature of the material.
- The Resistance “R” is dependent on the Temperature of the conductor.
Specific resistance of a material / Resistivity
- Specific resistance is defined as the resistance offered per unit length and unit cross-sectional area when a known amount of voltage is applied.
- R=ρ l/A , ρ=specific resistance, l=1m, a=1m, then R = ρ
Conductance of a material
The reciprocal of the resistance of a conductor is called its conductance. Unit of conductance is mho / Siemen
Conductance, G = 1/R
Conductivity
The reciprocal of the resistivity of a conductor is called its conductivity. Conductivity, σ = 1/ ρ
σ = 1/ ρ = L/ AR = 1/R x L/A = GL/A = mho meter / meter2 = mho/meter.
Unit of conductance is mho/meter or Siemen/meter.
Different Types Resistors:
Resistors are mainly two types Fixed resistors and variable resistors. A fixed resistor is one whose value remains constant under normal conditions.
Variable resistors are used to vary the amount of current for a circuit. Variable resistors are called Rheostats and Potentiometers.
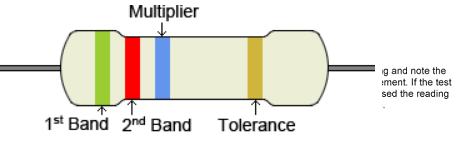
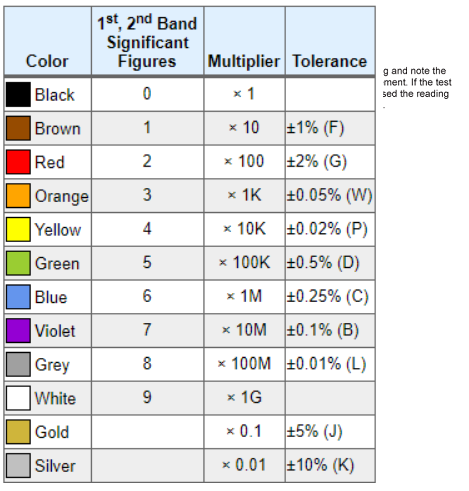
colour code:
It is not practical to print the resistance value on the resistors due to its small size, there for a method called colour code is adopted. The resistance values are generally printed on the body of bigger resistors like wire wound and metal film like resistor. But for the carbon resistor the values are colour coded since its size is very small to print. The value directly on the body of resistors. Colour coding is standardization by electronic industry association (EIA) colour bands are marked on the surface on the resistors. From one end the first band gives the first significant digit, second value gives the second significant digit of the resistance value and third band gives the multiplier and fourth band represents the tolerance in percentage value.
To identify resistor value and tolerance use colour code.
Using colour code:
- Hold the resistor so that the colour bands are in the left end of the resistor. Write down the numeric value of the first colour band.
- Write down the numerical value of the second colour band at the right side of the first numeric.
- Read the numeric value of the third colour band and write down those many zeros at the right side of the second numeric.
- Repeat the procedures for various resistors.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM


Recent Comments