Different types of insulators used in AC distribution system.
Types of insulators used in AC distribution system.
Overhead line conductors should be supported on the poles or towers with the help of insulators. The insulator provide necessary insulation between the line conductors and supports and thus prevent the leakage current from conductors to earth.
Properties of Overhead line insulators:
- High mechanical strength in order to withstand the conductor load, wind load etc.
- High electrical resistance in order to minimize the leakage currents
- High relative permittivity of insulating material so that the dielectric strength is high
- High ratio of puncture strength to flashover
- Insulating materials must be free from unwanted impurities.
Most commonly used material for overhead line insulators is porcelain. But glass, steatite and some other special composite material may also be used sometimes.
Types of insulators used in overhead
For the successful operation of power lines, proper selection of insulators is very essential. There are several types of overhead line insulators. Most commonly used types are
- Pin type insulators
- Suspension type insulators
- Strain insulators
- Shackle insulators
Pin type insulators
- Pin type insulators or pin insulators are popularly used in electric distribution systems up to 33 kV voltage level.
- A pin insulator is usually made from porcelain, but glass or plastic may also be used in some cases.
- They are secured on the cross arms of the pole to carry power lines. There is a groove on the upper end of a pin insulator for housing the conductor. Conductor wire is passed through this groove and secured by binding with the same wire as of conductor.
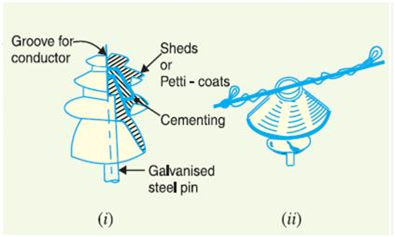
- A wet pin insulator may provide a path for current to flow towards the pole. Pin insulators are designed with Rain sheds / Petticoats to overcome the problems of conduction of wet insulator.
- Beyond operating voltage of 33kV, pin insulators become too bulky and uneconomical.
Suspension type insulators
- For voltages higher than 33 kV, suspension insulators are used.
- A suspension insulator consists of a number of porcelain discs connected to each other with metal links in the form of a string.
- Line conductor is suspended at the bottom end of the suspension string which is secured to cross-arm of the tower.
- Each disc in a suspension insulator string is designed for a low voltage, say 11 kV. The number of discs in a string depends on the working voltage. Suspension insulators are preferred for transmission lines.
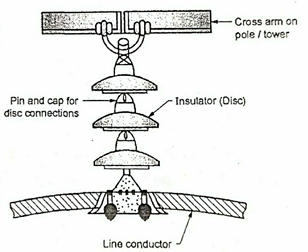
Advantages of suspension insulators
- Suspension insulators are cheaper than Pin insulators for voltage beyond 33KV.
- Each unit of disc is designed for a low voltage, say 11 kV. Hence, depending upon the working voltage, desired number of discs can be connected in series to form an insulator string suitable for particular voltage.
- If any of the discs in insulator string is damaged, it can be replaced easily. Replacement of the whole string is not required.
- In case of increased demand on the line, the line voltage can be increased and the additional insulation required for the raised voltage can be easily provided by adding the desired number of discs in the insulator strings.
- As the line conductors are suspended by suspension strings, they run below the earthed cross-arms of the towers. This arrangement provides partial protection from lightning.
- The suspension arrangement provides greater flexibility to the line. Suspension insulators are allowed to swing so that they can take up the position where mechanical stresses are minimum.
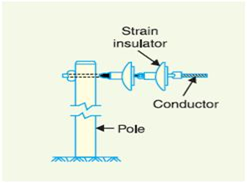
Strain insulators
- At a dead end of a transmission line, river bending or at a corner or sharp curve, the transmission line is subjected to a great tensile load.
- For high voltage transmission lines, stain insulator consists of an assembly of suspension insulators. In this case, the suspension string is arranged horizontally and the insulator discs are in vertical plane. Two or more suspension strings can be assembled in parallel to sustain greater tensions.
- For low voltage lines (less than11 kV), shackle insulators are used as strain insulators.
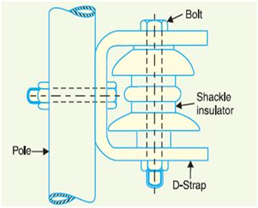
Shackle insulators:
- Shackle insulators are used in low voltage distribution lines as strain insulators.
- A shackle insulator can be used vertically as well as horizontally and it can be directly fixed to a pole with a bolt or to the cross arm.




Recent Comments