Fundamentals of AC System
PART A -2 Marks Questions
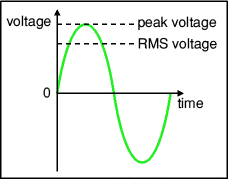
1.Define RMS value of an alternating current?
The RMS value of an alternating current is that steady current (dc) which when flowing through a given resistance for a given time produces the same amount of heat as produced by the alternating current when flowing through the same resistance for the same time.
Ir.m.s = 0.707 Io
2.Define form factor of an alternating current?
The ratio of RMS value to the average value of an alternating quantity.
FORM FACTOR = RMS VALUE / AVERAGE VALUE
3,Define Maximum value / Peak value of an alternating current?
It is the maximum value attained by an alternating quantity.
4. State power factor of an AC circuit?
It is the ratio of the power delivered to an AC circuit compared to the apparent power that the source must supply.
Power factor = R/Z = Resistance / Impedence
OR Power factor = cosine of angle between V and I
5. Draw the impedance triangle.?
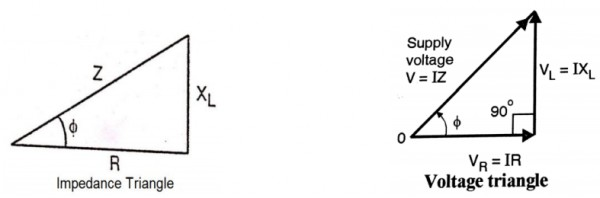
6. List any two power factor correction equipment?
- Static capacitors
- synchronous condenser
- phase advancers
7. State condition for resonance and frequency in series AC- circuit?
Series circuit is said to be resonance when the circuit power factor is unity ie, XL=XC
Frequency at which it occur is called resonance frequency, ,fr

8. Define poly phase.?
A polyphase electrical system, circuit, or device has generator is arranged to have two or more separate windings displaced from each other by equal electrical angles of the same frequency.
9. Define phase sequence?
The order in which the voltages in the three phase (coils) reach their maximum positive values is called the phase sequence.
10. What will be the power when ac passes through a pure inductance circuit ?
The average power in a pure inductor always zero.
11. Write the equation for finding 3 phase AC power?
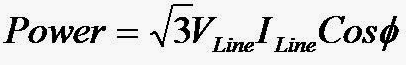
12. Define capacitive reactance?
Capacitive reactance ( XC) is a measure of a capacitor’s opposition to. AC (alternating current).
13. Define Q factor of a coil?
The ratio of the inductive reactance of a coil to its resistance at a given frequency is known as Q factor of the coil.
Q factor = XL / R
14. Write any two advantages of two wattmeter method of 3 phase power measurement?
The advantages of the two wattmeter method are: It uses two wattmeters instead of three. It can be used for purely resistive, resistive-capacitive loads, or resistive-inductive loads. It can be used for loads connected in delta or in wye.
PART B- 6 Marks Questions
1.List the advantages of AC over DC supply?
- AC supply is transmitting over long distances. AC can be transmitted using step up transformers but direct current or dc can not be transmitted by this method.
- The ac is easy to generate than dc.
- It is cheaper to generate ac than dc.
- The ac generators have higher efficiency than dc.
- The loss of energy during transmission is negligible for ac.
- The ac can be easily converted into dc.
- The variation of ac can easily be done using transformers either step up or step down.
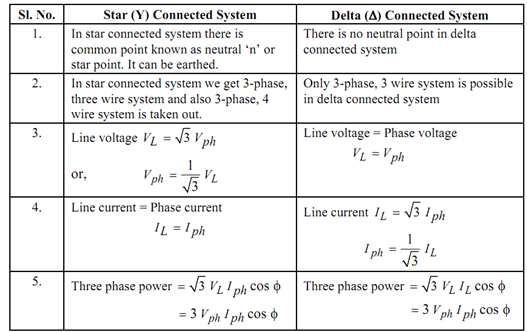
2.Distinguish between star and delta connection?
3. Draw and explain power triangle?
Power Triangle is the representation of a right angle triangle showing the relation between active power, reactive power and apparent power.
When each component of the current that is the active component (Icosϕ) or the reactive component (Isinϕ) is multiplied by the voltage V, a power triangle is obtained shown in the figure below:
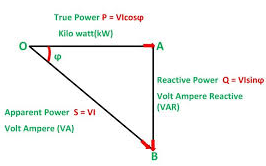
The power which is actually consumed or utilized in an AC Circuit is called True power or Active Power or real power. It is measured in kilowatt (kW) or MW.
The power which flows back and forth that means it moves in both the direction in the circuit or reacts upon it, is called Reactive Power. The reactive power is measured in kilovolt-ampere reactive (kVAR) or MVAR.
The product of root mean square (RMS) value of voltage and current is known as Apparent Power. This power is measured in KVA or MVA.
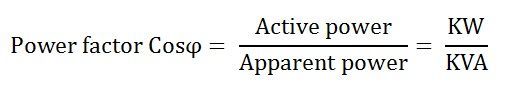
4. List the various methods used to measure 3-phase power?
- Single wattmeters method
- Two wattmeters method
- Three wattmeter method.
Single wattmeters method:
Limitation of this method is that it cannot be applied on unbalanced load. So under this condition we have

Two wattmeters method: Two Wattmeter Method can be employed to measure the power in a 3 phase, three wire star or delta connected the balanced or unbalanced load. In Two wattmeter method the current coils of the wattmeter are connected with any two lines, say R and Y and the potential coil of each wattmeter is joined on the same line, the third line.
Star connection
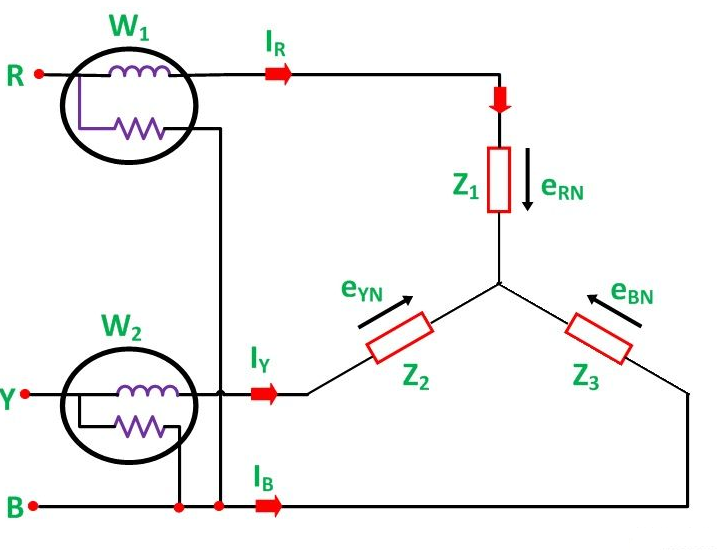
Delta connection
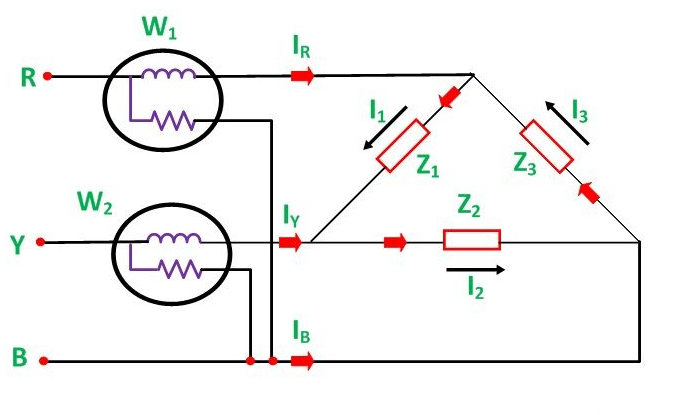
Three wattmeter method: Three Wattmeter method is employed to measure power in a 3 phase, 4 wire system.However, this method can also be employed in a 3 phase, 3 wire delta connected load, where power consumed by each load is required to be determined separately.
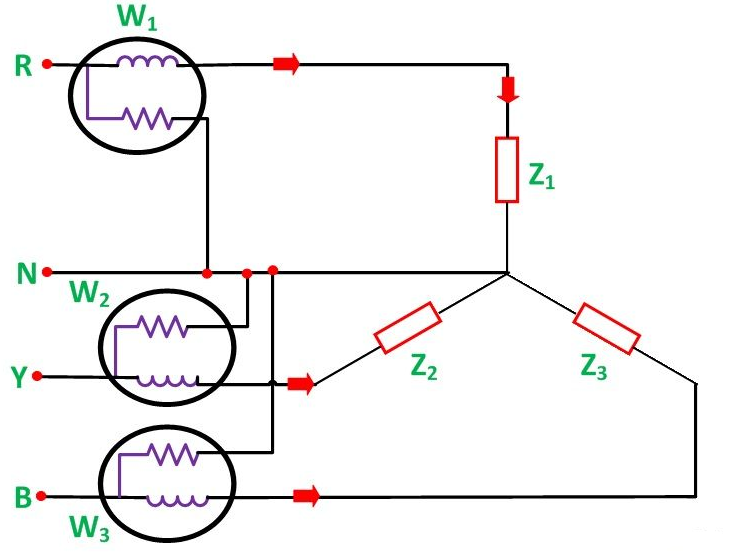
The total power in a Three wattmeter method of power measurement is given by the algebraic sum of the readings of Three wattmeters. i.e.
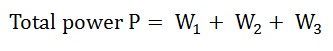
5.Compare balanced and unbalanced load?
Balanced load, in 3 phase system is a condition where all three phases (lines) carry same magnitude of current, with evenly spaced phase difference. If the load is star connected, with neutral as return path, this neutral will carry no current. This is so since vector sum of all three phase currents meeting at common neutral point is zero.
Unbalanced load, makes the lines / phases to carry different current magnitudes, and sum total of these at neutral point is not zero. Load in each phase is different, carrying ts own current. Neutral in this case carries the net unbalanced current .
PART C- 7/8 Marks Questions
1.[,ist the methods of improving power factor?
- Static capacitors
- Synchronous condenser
- Phase advancers
Static capacitors : The power factor can be improved by connecting capacitors in parallel with the equipment operating at lagging power factor. The capacitor (Static capacitor) draws a leading current and completely neutralises the lagging reactive component of load current. This raises the power factor of the load. For 3 phase loads, capacitor connected in delta or star.
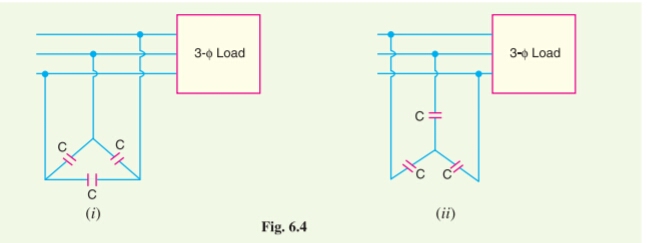
Synchronous condenser :An overexcited synchronous motor to improve the poor power factor of a power system. The main advantage of using synchronous motor is that the improvement of power factor is smooth.When a synchronous motor runs with over-excitation, it draws leading current from the source.. three-phase system, we connect one three-phase synchronous motor is parallel with the supply and run it at no load.It takes leading current which partially neutralises the lagging reactive component of the load, thus the power factor is improved.

Phase advancers : Phase advancers are used to improve the power factor of induction motors as by Static capacitors and Synchronous condenser.Phase advancer is a simple AC exciter which is connected on the main shaft of the motor and operates with the motor’s rotor circuit for power factor improvement. Phase advancers are used to improve the power factor of induction motors. The low power factor of an induction motor is due to the fact that its stator winding draws exciting current which lags be-hind the supply voltage by 90 degrees. If the exciting ampere turns can be provided from some other a.c. source, then the stator winding will be relieved of exciting current and the power factor of the motor can be improved. . It provides exciting ampere turns to the rotor circuit at slip frequency. By providing more ampere turns than required, the induction motor can be made to operate on leading power factor like an over-excited synchronous motor.
2.List and explain the advantages of poly phase system?
- Three phase equipment is more readily available than single phase;
- Three phase equipment typically have many more options available, e.g. size, power rating, bells and whistles, etc.
- Three phase systems are easier to get equipment to adapt. Meaning, if the voltage rating is not exactly matching your line voltage, its easier to find ways in a three phase system to make it work. Single phase, you’re stuck.
- Lower amps are consumed by equipment, which means smaller wires can be run, and lower cost of cabling.
- Lower power losses, i.e. more efficient equipment.
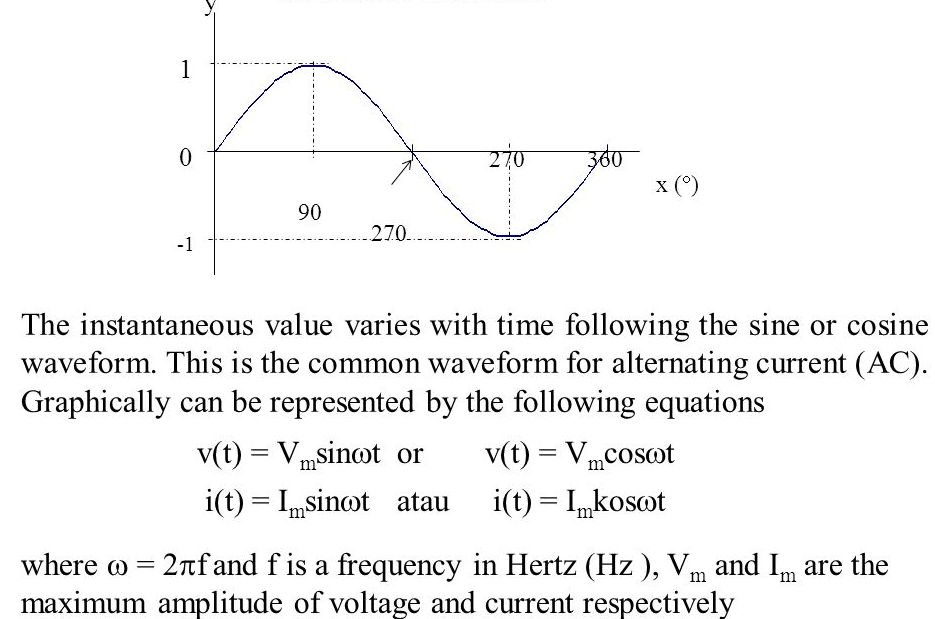
3.Derive the equation for instantaneous value of alternating voltage?
4. Define the following :
(i Instantaneous value
(ii) Maximum value
(iii) Average value
Instantaneous value : The instantaneous value is the value of an alternating quantity (ac voltage, ac current or ac power) at a particular instant of time in a cycle. The instantaneous value of any variable quantity is designated by the smaller case letter of its symbol. For example, v for voltage, i for current, etc.
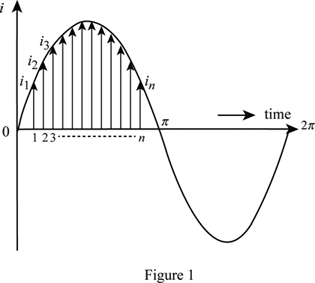
Maximum value : It is the maximum value/Peak value attained by an alternating quantity.

Average value: The average value of a waveform is the average of all its values over a period of time. Finding an average value over time means adding all the values that occur in a specific time interval and dividing the sum by that time.
Average value = Total area under curve for time T / Time T
5. Define the terms i) amplitude ii) Frequency iii) Time period?
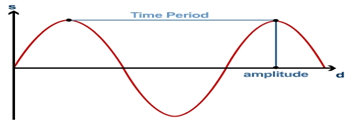
Amplitude : It is the maximum value ( positive or negative half cycle) attained by an alternating quantity.
Time period : A time period (denoted by ‘T’ ) is the time taken for one complete cycle of an alternating quantity. As the frequency of a wave increases, the time period of the wave decreases.
Frequency : It is the number of cycles that occur in one second.unit is hertz.
6.Explain relation between :
(D Time period and frequencv
(ii) Angular velocity and frequency
(ut) Frequency and speed?
Time period and frequency: Frequency, f, is how many cycles of an oscillation occur per second and is measured in cycles per second or hertz (Hz). The period of a wave, T, is the amount of time it takes a wave to vibrate one full cycle. These two terms are inversely proportional to each other:
ie, f = 1/T and T = 1/f
Angular velocity and frequency : Angular velocity ω, also called radial or circular frequency, measures angular displacement per unit time. Its units are therefore degrees (or radians) per second
ω = 2πf or 2πT
where f is frequency of rotation and T time period of rotation.
Frequency and speed : f = PN/120
where f is frequency of electric supply, P is number of poles in the motor and N = speed in rpm.
7. An alternating current i is given by , i = 141.4 sin 314 t. Find i) the maximum value ii) Time period iii) Frequency iv) the instantaneous value when t is 3 ms?
i) the maximum value = 141.4 A
ii) Frequency , f = ω/2π = 314/2π = 50 Hz
iii) Time period = T=1/f = 1/50 = 0.02 s
iv) the instantaneous value when t is 3 ms = i = 141.4 sin 314 t = i = 141.4 sin 314 x 3 x 10^-3 sec = 114.35 A




Recent Comments