Electrical Engineering Materials
I Unit – Conducting Materials
1. List any two conducting Materials?
The material which allow the flow of charges (electrons) through them are called conducting materials.
Silver, copper, Aluminum, Gold
2. Briefly describe the Electrical property of Conducting Materials?
- Resistivity: It is the measure of the resistance offered by a material having unit length and cross section area to electric conduction. A good conducting material, having resistivity must be low.
- Conductivity: It is indicate of the ease with which a material is capable of conducting electric current (charges/heat). A good conducting material, having high con ductility.
- Temperature Co-efficient of Resistance: The change in resistance of a material per ohm per degree change in temperature is called Temperature Co-efficient of Resistance. This means that the change of resistance with change in temperature should be low.
- Contact Resistance: It refers to the resistance of an interface between two conductors.
- Dielectric Strength: It is the maximum electric field that a material can with stand without experiencing failure of its insulating properties.
- Electric energy dissipated in the form of heat must be low.
3. Briefly describe the Mechanical property of Conducting Materials?
- Stress: It is the amount of force sustained by the material per unit cross sectional area.
- Strain: It is the change (Elongation or Contraction) in length undergone by the material per unit of its original length. Stress α Strain.
- Strength: It is the ability of a material to sustain external force or loads which act upon it during its working, without distortion.
- Ductility: It is the ability of the material with which it can be drawn into wires and bent without fracture.
- Malleability: It is the ability of the material by virtue of which a material may be hammered or rolled into thin sheets without rupture.
- Hardness: It is the property of the material to resist penetration.
- Brittleness: Lack of ductility is called Brittleness.
- Toughness: it is the strength with which the material opposes rupture.
- Elasticity: It is the property by which a material regains its original shape on on removal of load.
- Plasticity: It is the property that enables the formations of permanent deformation in a material.
4. List out the Specification of Conducting Materials?
When a particular material is selected for a job the specification should be followed precisely to obtain desired performance. Specifications of conducting materials include the following,
- Specific Resistance
- Composition of materials.
- Specific heat capacity.
- Properties of material (Electrical, Mechanical, Physical, Magnetic…)
- Co-efficient of linear thermal expansion.
- Physical dimensions and shape.
- Factor of safety.etc..
5. List out the Desirable properties of a good Conductor?
- Low Specific Resistance.
- High electrical conductivity.
- High tensile strength in order to withstand mechanical stresses.
- Relatively lower cost without compromising much of other properties.
- Lower weight per unit volume.
6. List out the Properties & Applications of Silver?
Properties
- It is extremely white colour with high metallic luster.
- Pure silver has high electrical conductivity.
- It is highly malleable and ductile.
- It has highest heat conductivity among metals.
- It has high corrosion resistance.
- It has high tensile strength & Toughness.
- Its hardness and rigidity less.
- Its melting point is 961 0C.
Applications:
- It is used for silver electroplating.
- It is used for making Circuit breaker contacts.
- It is used for making relay contacts.
- Used in special electrical instruments.
- It is also used for making ornaments.
- Used for making commutator segments of small dc motors.
- For brushes and collector ring of dc motors silver graphite alloys are used.
7. List out the Properties & Applications of Copper?
Properties:
- Copper is most widely used metal, because of its high conductivity and low resistivity.
- Copper is a Nonmagnetic metal and high current density.
- It is Reddish brown colour with high metallic luster.
- It has high resistance to corrosion.
- It is highly malleable and ductile.
- It can easily soldered and welded at red heat.
- Its melting point is 10840 C.
- Electrical resistivity is 1.682 micro ohm cm.
- Its tensile strength varies from 3 to 4.7 tonnes / cm2.
- It forms important alloys like brass, bronze….
- Its boiling point is 25950 C.
- It has low contact resistance.
- It oxidizes above 1800 .
- It has high tensile strength & Toughness.
Applications:
- Copper is mainly used for wires, cables, Winding of generators and transformers, overhead conductors, bus bars etc.
- It is used for contacts material for control relays.
- It is also used for motor starter switches and tap changers.
- Hard drawn copper conductors is mechanically strong with high tensile strength 40 kg/mm2. It is used for making commutator segments, overhead lines and bus bars.
- Annealed copper (soft copper) is mechanically weak, tensile strength of 20 kg/mm2. it is easily shaped into any form.
8. List out the Properties of Gold?
- Its appearance is dark yellow known as golden colour.
- It has attractive metallic luster and colour.
- It has high electrical conductivity and heat conductivity.
- It is highly malleable and ductile.
- It has high corrosion resistance. Corrosion effect is almost negligible.
- It has high tensile strength & Toughness.
- Its hardness and rigidity less.
- Its melting point is 1063 degree C.
- It is also used for making ornaments.
9. List out the Properties of Aluminum?
- Pure Aluminium is silvery colour with metallic luster.
- It is cheap and light as compared to copper, but it has much smaller conductivity and Tensile strength than copper.
- It is highly malleable and ductile.
- It has highest heat conductivity among metals.
- It is good conductor of heat and electricity.
- It can be rolled, forged, drawn.
- It has high corrosion resistance.
- It forms useful alloys with iron, copper, zinc and other metals.
- It is nonmagnetic.
- It cannot be soldered or weldered easily.
- It has high contact resistance.
- Its melting point is 658 0C.
- Its Boiling point is 20570 C.
- The conductivity of aluminium is 75% of that of copper.
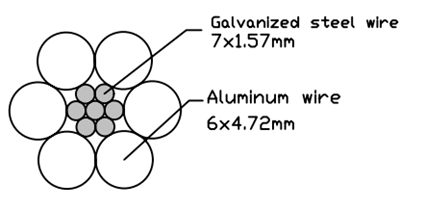
10. Write a short note about ACSR Conductors?
- Its Full form is Aluminium conductor steel reinforced.
- It has central core of Galvanized steel core with one or more layers of aluminum wires stranded outside.
- Reinforcement is done to increase the tensile strength of aluminum conductor.
- Steel wire is galvanized to prevent rusting and electrolytic corrosion.
- The ultimate tensile strength of such conductor is considerably larger than that of equivalent copper conductors and its weight is still about 25% lesser.
- Conductor gives less sag because of its less weight and high tensile strength.
- ACSR conductor has larger diameter than any other conductor of same resistance which helps to reduce corona.
- It is used for transmission lines where the span is more than 100 meters.
11. List Advantages of ACSR Conductors?
- High mechanical strength due to central steel wire.
- Long spans are possible.
- Reduces the number poles and other equipment’s.
- No corona effect.
- Longer life is possible.
- Cost is less.
- Used for overhead transmission lines.
12. Short note about AAAC Conductor?
14. Compare the properties of Copper and Aluminium?
15. Compare ACSR & AAAC Conductor?
Alloy of Tin & Lead (63% & 37%)
3. Write any two desirable Characteristics of Fuse element?
- Low melting point ( like tin & lead)
- High conductivity (like silver & copper..)
- Free from deterioration due to oxidation ( silver..)
- Low cost (eg: lead, tin , copper..)





Recent Comments