TIG welding
TIG welding(Gas Tungsten Arc Welding)
Gas tungsten arc welding is an arc welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode and an inert gas for arc shielding.
It is also known as GTAW,
Equipments use in TIG:
- Gas supply (cylinder)
- Electrical power source
- (AC/DC)
- Electrode holder, torch or gun
- Connection cables
- Hose (for gas supply)
- Tungsten electrode
- Coolant
- Filler rods
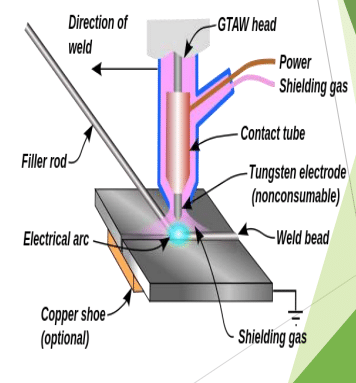
Working principle:
- An arc is established between the end of a tungsten electrode and the parent metal at the joint line..
- A constant-current welding power supply is used to produces energy which is conducted across the arc through a column of highly ionized gas and metal vapors known as a plasma.
- Argon and helium are the most commonly used shielding gases.
Characteristics of the TIG welding process:
- Uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode during the welding process,
- Uses a number of shielding gases including helium (He) and argon (Ar),
- Is easily applied to thin materials,
- Produces very high-quality, superior welds,
- Welds can be made with or without filler metal,
- Provides precise control of welding variables (i.e. heat),
- Welding yields low distortion,
- Leaves no slag or splatter.
Quality:
- Gas tungsten arc welding affords greater control over the weld area than other welding processes,
- It can produce high-quality welds when performed by skilled operators.
- Maximum weld quality is assured by maintaining cleanliness—all equipment and materials used must be free from oil, moisture, dirt and other impurities, as these cause weld porosity and consequently a decrease in weld strength and quality.
Applications:
- TIG is most commonly used to weld thin sections of stainless steel and nonferrous metals such as aluminum, magnesium, and copper alloys.
- The aerospace industry is one of the primary users of gas tungsten arc welding, It is also frequently employed to weld small-diameter, thin-wall tubing such as those used in the bicycle industry.
- TIG is often used in piping of various sizes.
- Aerospace industry uses lite metals (Aluminum and its alloy) thin sheet and need high quality welding. So TIG is more suitable for it.
- Tig welding also used for others industrial purposes. Such as for various piping , Joining thin material in automobile industry.
Advantages of TIG Welding:
No flux is used.
Welding is smooth and sound with fewer scatters.
Very suitable for high quality welding in thin materials.
Very good process for welding nonferrous metals and stainless steels.
The surface finish is good.
The equipments are portable
limitations of TIG Welding:
Tungsten inclusion is hard and brittle.
Equipment costs are high
In steel welding operations, TIG is slower and the most costly one.
Filler rod end, if by chance comes out, then inert gas shield can cause weld metal contamination.




Recent Comments