Thermal Power Stations (Steam Power Stations)
A generating station which converts the heat energy of coal combustion into electrical energy is known as a steam power station.
Steam produced in the boiler by utilizing the heat of coal combustion. The steam is then expanded in the prime mover (steam turbine) and is condensed in a condenser to be fed into the boiler again. The steam turbine drives the alternator which converts mechanical energy of the turbine into electrical energy.
The main components of the power station are,
1. Coal and ash handling arrangement:
The coal is transported to the power house and is stored in coal storage plant. It is then delivered to the coal handling plant, where it is crushed into small pieces called Pulverization. In order to increase its surface exposure, gives fast combustion without using large quantity of excess air. The pulverized coal is fed to the boiler by belt conveyors. The coal is burnt in the boiler and the ash produced after complete combustion of coal is removed to the ash handling plant and then delivered to the ash storage plant for disposal. Pulverisation advantages are,
- In order to increase its surface exposure, gives fast combustion without using large quantity of excess air.
- Low grade coal also can be burnt.
- Boiler can be started quickly.
- No ash handling problems.
- The furnace volume required is less.
- The operation troubles are less.
- Large quantity of steam generation is possible.
- Fast response to load changes.
2. Steam generating plant:
This is an important part of steam power station, it includes boiler, boiler furnace, super heater, economizer, air pre-heater…
a) Boiler : A boiler is closed vessel in which water is converted into steam by utilizing the heat of coal combustion. Steam boilers are broadly classified into the following two types, Water tube boilers & Fire tube boilers. In a water tube boiler, water flows through the tubes and the hot gases of combustion flow over these tubes. On the other hand, in a fire tube boiler, the hot products of combustion pass through the tubes surrounded by water.
b) Boiler furnace: A boiler furnace is a chamber in which fuel is burnt to liberate the heat energy. The boiler furnace walls are made of refractory materials such as fire clay, silica, kaolin etc.
c) Super heater: A super heater is a device which super heats the steam, it further raises the temperature of steam. This increases the overall efficiency of the plant. A super heater consists of a group of tubes made of special alloy steels such as chromium molybdenum and placed on the way to the chimney. The steam produced in the boiler is wet & passed through the super heater, it is superheated by the heat of flue gases on their way to chimney. Functions are,
- Improve the overall efficiency.
- Reduce the steam consumption per given output.
- Eliminates the erosion of steam turbine blades due to the absence of moisture.
d) Economiser: It is a device which heats the feed water on its way to boiler by deriving heat from the flue gases. An economizer consists of a large number of closely spaced parallel steel tubes connected by headers of drums. The feed water flows through these tubes and the flue gases flow outside. A part of heat of flue gases is transferred to feed water, thus raising the temperature of the latter. This results in raising boiler efficiency, saving in fuel and reduces stresses in the boiler due to high temperature of feed water.
e) Air Pre-heater: Super heaters and economizers generally cannot fully extract the heat from flue gases. ie, pre – heaters are employed which recover some of the heat in the escaping gases. The function of an air pre-heater is to extract heat from the flue gases and give it to the air being supplied to furnace for coal combustion. This raises the furnace temperature and increases the thermal efficiency of the plant.
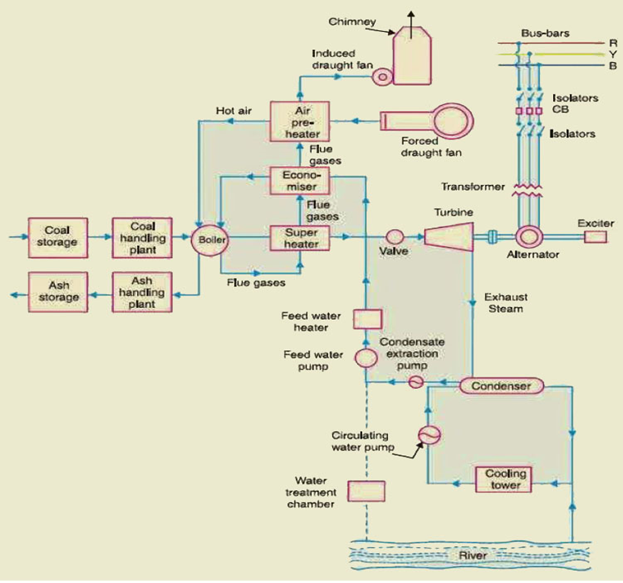
3. Steam turbine:
The high pressure high temperature superheated steam from the super heater fed to the steam turbine through main valve. The steam energy passing over the blades of turbine is converted into mechanical energy.
4. Alternator:
The steam turbine coupled to an alternator. The alternator converts mechanical energy of turbine into electrical energy. The electrical energy output is delivered to the bus bars through transformer, circuit breaker, isolators.
5. Cooling Arrangement:
The exhausted steam from the turbine, goes to the condenser which condenses the exhausted steam by means of cold water circulation and maintain a pressure at the exhaust lower than atmosphere. Water is drawn from a river, canal and is circulated through the condenser. The circulating water takes up the heat of the exhausted steam and it becomes hot.
6. Feed water:
The condensate from the condenser is used as feed water to the boiler by using feed water pump. The feed water on its way to the boiler is heated by water heaters and economizer. This helps the improving overall efficiency of the plant.




Recent Comments